INDUSTRY NEWS
QC-CMM
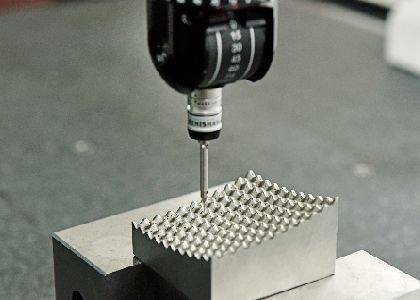
CMM is a device that measures the geometry of physical objects by sensing discrete points on the surface of the object with a probe. Various types of probes are used in CMMs, including mechanical, optical, laser, and white light. CMMs typically specify a probe's position in terms of its displacement from a reference position in a three-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system (i.e., with XYZ axes). In addition to moving the probe along the X, Y, and Z axes, many machines also allow the probe angle to be controlled to allow measurement of surfaces that would otherwise be unreachable.
